Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) has become increasingly popular as more men recognize the symptoms of low testosterone and seek treatment options. This guide provides an overview of what TRT is, how it works, and what you can expect from treatment.
What is Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
Testosterone Replacement Therapy is a medical treatment designed to increase testosterone levels in men who have low testosterone (hypogonadism). It’s important to understand that TRT is specifically for treating clinically low testosterone levels, and not a general anti-aging solution. Testosterone levels naturally decline by about 1% per year after age 30 (Healthline).
Testosterone is a vital hormone that plays a key role in:
- Muscle mass and strength
- Bone density
- Fat distribution
- Red blood cell production
- Sex drive
- Mental clarity and mood
When natural testosterone levels fall below normal ranges, TRT can help restore them to optimal levels.
Common Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Many men seek TRT after experiencing symptoms such as:
- Persistent fatigue
- Reduced sex drive (libido)
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased muscle mass
- Increased body fat
- Depression or mood issues
- Cognitive difficulties
- Sleep disturbances
If you're experiencing multiple symptoms from this list, speaking with a healthcare provider about testosterone testing may be a good first step.
TRT Treatment Methods
There are several ways to administer testosterone replacement therapy:
Injections
The most common and often most effective method, involving intramuscular or subcutaneous injections of testosterone cypionate or enanthate, typically every 1-2 weeks (MyFitMed).
Topical Gels and Creams
Applied daily to the skin where testosterone is absorbed. Less invasive but requires daily application and careful handling to avoid transferring to others (Cleveland Clinic).
Patches
Testosterone patches are applied daily to the skin, providing a steady release of the hormone.
Pellets
Small pellets implanted under the skin that slowly release testosterone over 3-6 months.
Benefits of TRT
Clinically proven benefits of TRT include improved libido, increased energy, enhanced mood, better muscle strength, and increased bone density (PubMed). The Cleveland Clinic emphasizes consistent TRT’s ability to significantly improve sex drive, mood, and energy in men with genuine testosterone deficiency (Cleveland Clinic).
Monitoring Your TRT
Proper monitoring is essential for successful TRT. Clinical guidelines recommend regular blood tests and check-ups, typically 3-6 months after starting therapy and annually thereafter. Important tests include (American Family Physician):
- Total and free testosterone levels
- Estradiol (a form of estrogen, important due to testosterone conversion)
- Hematocrit and hemoglobin (to monitor red blood cell levels)
- Lipid panel
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
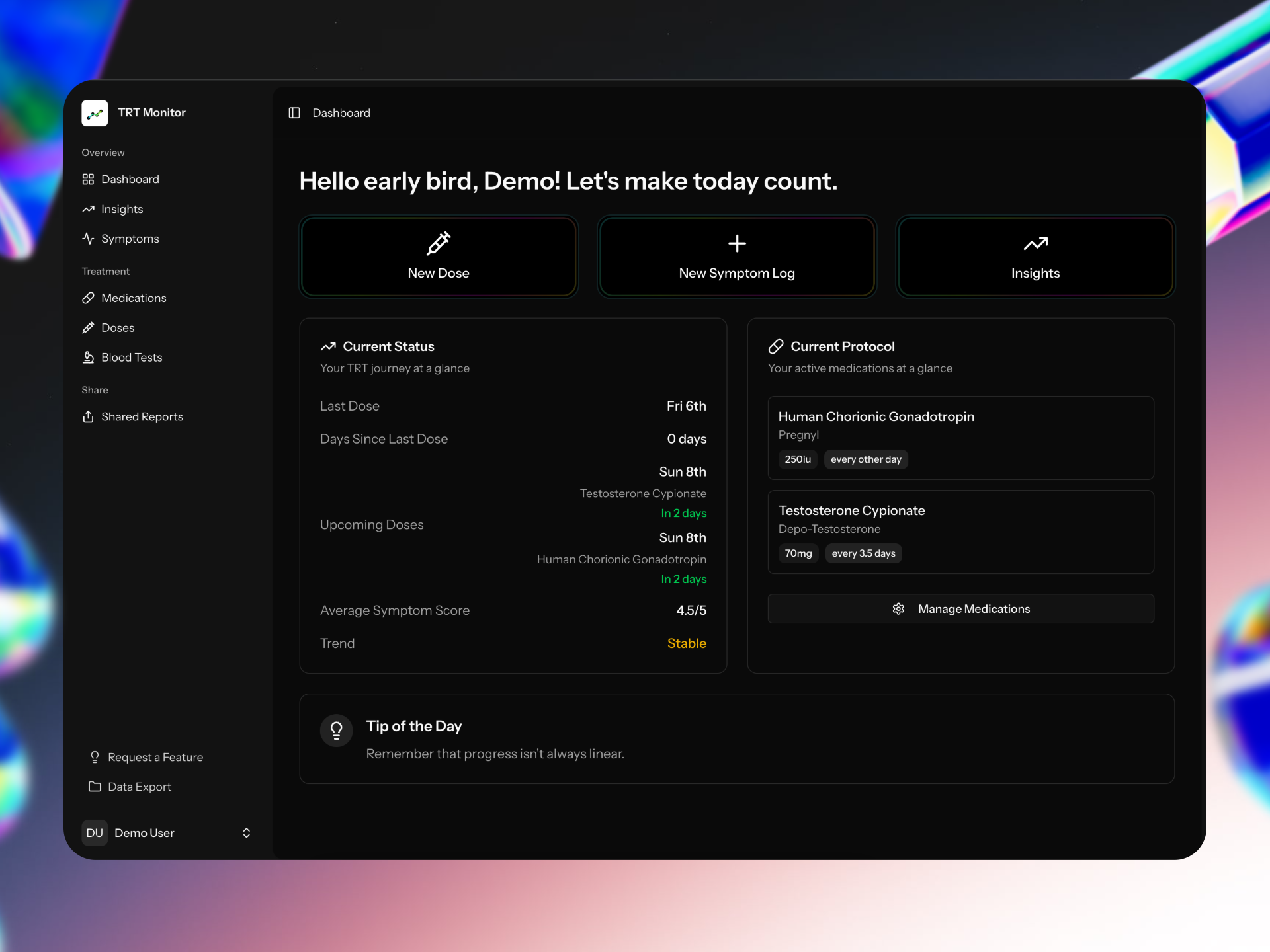
Tracking symptoms systematically, like using the TRT Monitor app, can also help assess how well your treatment is working beyond just blood test results.
Potential Side Effects
While TRT provides significant benefits for many men, potential side effects include (Mayo Clinic):
- Increased red blood cell count (polycythemia)
- Acne or oily skin
- Fluid retention
- Breast enlargement (gynecomastia)
- Testicular shrinkage and reduced fertility
- Mood swings
- Potential exacerbation of sleep apnea
- Prostate growth (benign prostatic hyperplasia)
TRT may also increase estradiol (estrogen) levels due to aromatization in fat tissue, possibly causing bloating or mood changes (PubMed). Medical supervision and regular monitoring are crucial to manage these risks effectively.
Further Reading
For more detailed information about TRT’s benefits and risks, consider visiting the Mayo Clinic’s TRT overview or the Cleveland Clinic’s guide to male hypogonadism.
Conclusion
Testosterone Replacement Therapy can be life-changing for men with clinically low testosterone levels. With proper medical supervision, appropriate dosing, and regular monitoring, TRT can significantly improve quality of life, energy levels, body composition, and overall wellbeing.
If you're considering TRT, consult with a healthcare provider specializing in hormone optimization to determine if it's right for you and create a personalized treatment plan.
References and Further Reading:
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy Overview (Healthline)
- Testosterone therapy: Potential benefits and risks (Mayo Clinic)
- Optimizing Testosterone Injection Frequency (MyFitMed)
- American Family Physician - Testosterone Therapy
- Low Testosterone: Symptoms & Treatment (Cleveland Clinic)
- Estrogens in Men: Clinical Implications (PubMed)
- Risks of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (PubMed)